Unlocking the potential of energy efficiency in the real estate industry: Strategies for reducing consumption and saving costs
To create a sustainable real estate industry and decrease emissions, owners, managers, and caretakers need to adopt a holistic and total approach to energy reduction.
Discover ways to save energy through insulation, heat pumps, updated electrical systems, green roofs, certifications such as LEED, and AI-based technology.
Numerous solutions to reduce CO2 emissions and increase energy savings
As the world looks for ways to combat the climate crisis, investors and venture capitalists are focusing on innovative technologies such as climate tech, nature tech, and proptech to find new solutions. Simple changes such as using energy-efficient appliances and lighting can greatly reduce electricity consumption and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, is also a highly effective method to decrease carbon emissions.
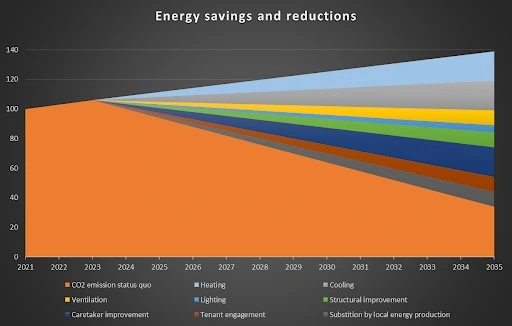
Main factors to increase energy efficiency
- Heating, including heat pumps
- Cooling
- Ventilation
- Control of lightning
- Structural improvement
- Caretaker engagement in energy efficiency
- Tenant engagement
- Substitution by local and renewable energy
Buildings account for 40% of Europe’s energy consumption in Europe according to European Public Real Estate Association (EPRA). It is difficult to provide an exact answer regarding the amount of energy that can be saved. The increased electricity a building uses each year can vary greatly depending on several factors.
These factors might include
- Building design, such as the size and age of the buildings
- The type of heating and cooling systems it uses
- The efficiency of heating systems, grids, appliances, heat pumps and lighting, and energy-efficient technologies and appliances
- Tenants and the behavior of the people who live or work in the building
- The rate of electricity consumption in buildings can vary depending on the region and climate in which the building is located and the availability of renewable energy sources.
To determine the potential energy savings from implementing energy-efficient upgrades and improvements, please reach out to our team.
How could a company and building be “Paris” aligned and below 2 degrees celsius?
“Paris-aligned” is a term that refers to buildings that are designed and constructed in accordance with the goals of the Paris Agreement. The Paris Agreement is an international treaty that was adopted in 2015 to address climate change and to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
To be “Paris-aligned,” a building would need to be designed and constructed in a way that reduces its greenhouse gas emissions and energy and the long-term impacts of climate change. This could include features such as high-efficiency insulation, renewable energy systems, and other measures that help to reduce the building’s carbon footprint.
The carbon emission baseline
A carbon emissions baseline is a reference point or starting point used to measure the number of carbon emissions produced by a particular activity or organization.
The carbon emissions baseline is typically established by measuring the number of carbon emissions produced over a certain period of time, such as a year.
This baseline can then be used to set goals for reducing carbon emissions and to track progress toward those goals. The concept of a carbon emissions baseline is often used in the context of climate change and efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
In general, most buildings will likely experience some increase in their electricity usage each year due to factors such as population growth and the increasing use of electricity-powered devices. In our model, we calculate a 3% increase level year-on-year. Maybe the Ukraine war with increased energy prices leading to people trying to save costs in energy will keep that number down.
The impact of energy-efficient heating systems and practices
According to a report by McKinsey, heating, and cooking in commercial and residential buildings account for a significant portion of global CO2 emissions, standing at 6 percent.
Implementing energy-efficient heating systems and practices can not only reduce energy consumption and costs but also decrease a building’s carbon footprint. For example, a building with good insulation in a cold climate can expect to see substantial energy savings by implementing energy-efficient heating systems.
The exact amount of savings will vary based on the building and its heating systems, but overall, implementing grid improvements for heat can lead to significant energy savings, potentially in the range of 10-20% or higher, depending on the specific circumstances.
How much energy savings do you get with heat pumps?
Heat pumps are a type of energy-efficient heating and cooling system that can provide significant energy savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. According to Energy.gov it is estimated that geothermal (or ground source) heat pumps can provide energy savings of 30-60% compared to electric resistance heating or fossil fuel-based heating systems. Additionally, heat pumps can also provide cooling during the summer months, further increasing their potential for energy savings.
How much energy yearly savings do you get in your buildings with grid improvement?
Improving the grid can help increase the efficiency and reliability of the power supply, which can help reduce energy losses and improve the overall efficiency of the system. This, in turn, can lead to energy savings for buildings that are connected to the grid. The exact amount of energy savings achieved will depend on many factors, including the specific details of the grid and the improvements being made, as well as the climate and weather conditions in the area.
What is demand response?
Demand response is a program or system in which building owners and operators agree to reduce their electricity usage during times of high demand on the grid. This can help prevent power outages and other problems on the grid and can also help reduce the need for expensive and polluting forms of power generation.
By participating in a demand response program, building owners and operators can receive financial incentives for reducing their electricity usage during peak times and can also help support the stability and reliability of the power grid. The amount of energy savings achieved through demand response will depend on several factors, including the size and energy consumption of the building and the specific details of the demand response program.
Cooling and cooling compressors
Cooling compressors are a key component of many air conditioning and refrigeration systems. They are responsible for compressing refrigerant gasses, which increases their temperature and pressure. This, in turn, allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the air or water being cooled and then release that heat to the outside environment when it expands.
By using cooling compressors, air conditioning and refrigeration systems can effectively control the temperature and humidity of a building or space, which can help create a comfortable environment for occupants. However, cooling compressors can also be a significant source of energy consumption, so it’s important to use energy-efficient compressors and other components to minimize their impact on the environment and reduce energy costs.
Ventilation
AI-based IAQ
AI-based IAQ (indoor air quality) systems use artificial intelligence to monitor and manage the air quality in a building. These systems can use sensors and other data sources to collect information about the air quality in a building and then use AI algorithms to analyze the data and identify potential problems or issues.
By using AI-based IAQ systems, building managers and occupants can better understand the air quality in their buildings and take steps to improve it, if necessary. This can help create a healthier and more comfortable environment for occupants and may also help reduce the risk of health problems associated with poor air quality.
Lightning
Light control
Light control systems are technologies that allow building managers and occupants to control the lighting in a building more efficiently and effectively. These systems can use sensors, timers, and other technologies to automatically adjust the lighting levels in a building based on factors such as the time of day, working hours and the amount of natural light available, and the presence of occupants.
By using light control systems, building managers and occupants can reduce the amount of energy used for lighting, which can help save on energy costs and reduce the building’s carbon footprint. In addition, light control systems can help create a more comfortable and productive environment for occupants by providing the right amount of light for different tasks and activities.
Structural improvements like building design and energy-efficient technologies and appliances
Energy savings in LEED or REC?
LEED, or Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, is a building certification program that promotes sustainable design and construction.
LEED-certified buildings have been shown to emit 50% fewer greenhouse gases related to water consumption, 48% less related to solid waste, and 5% less related to transportation compared to traditional buildings. This demonstrates that adhering to LEED standards can have a significant impact on reducing a building’s overall environmental impact.
However, the exact amount of savings will vary depending on the specific design and construction of the building. It’s important to consult with a professional who is familiar with the LEED certification process to determine the potential energy savings for a specific building.
What are the pros and cons of insulated glass for buildings
Insulated glass, also known as double or triple-paned windows, can provide several benefits for buildings and commercial buildings. The main advantage is increased energy efficiency, as the layers of glass and the insulating gas between them can help to keep heat inside during the winter and outside during the summer. This can lead to significant savings on heating and cooling costs.
The main disadvantage of insulated glass is the initial cost, which can be higher than traditional single-paned windows. Additionally, if the sealed unit is damaged, it can be difficult and expensive to repair.
The most common gasses used in insulated glass are argon and krypton. These are not harmful and are unlikely to leak, but if the sealed unit is damaged, the gas can escape. This is not a significant risk, but it is something to keep in mind.
The critical role of caretakers in achieving energy savings
Caretaker engagement and insulation are some of the most effective ways to achieve energy savings and reductions by reducing the amount of heat. This can be done by adding insulation to the walls, attic, and other areas where heat may escape.
An engaged caretaker with the right digital tools is crucial for optimizing buildings. It is important to have caretakers involved and engaged in efforts to reduce energy use and save in the real estate sector. Humans can give tips directly to tenants about isolation and tricks on how to get a more energy-efficient building.
People can play a critical role in educating tenants about the benefits of insulation and potential energy savings and cost savings that can be achieved and explaining how they work and how to maintain them. While machines and AI can effectively optimize energy use in buildings, it is ultimately up to people to implement and maintain these systems and ensure they are working properly. This means that people play a critical role in achieving energy savings in buildings.
Tenant engagement, such as the behavior of building occupants
What is scope 3 in CO2 baseline
Scope 3 emissions, also known as indirect emissions, are those emissions that are a result of the activities of an organization but occur outside of the organization’s direct control. In the context of a carbon emissions baseline, scope 3 emissions would be those emissions that are not directly produced by the organization but are still a result of its activities.
Examples of scope 3 emissions might include the emissions produced by a company’s supply chain or those produced using a company’s products. To establish an accurate carbon emissions baseline, it is important to consider both direct and indirect emissions, including scope 3 emissions.
Substitution by local and renewable energy
The power of the sun: How solar panels can reduce energy bills and carbon footprint
Solar panels are a type of technology that converts sunlight into electricity. They are a renewable and clean energy source and can help reduce a building’s reliance on fossil fuels and associated carbon emissions. By installing solar panels on a building, you can generate electricity and potentially reduce your energy bills.
The amount of energy savings achieved will depend on several factors, including the size and efficiency of the solar panel system, the amount of sunlight the building receives, and the building’s energy consumption. In general, however, solar panels can be a great way to reduce a building’s carbon footprint and save on energy costs.
Exploring the energy savings potential of green roofs: Insulation, temperature regulation, and more
Green roofs, also known as vegetated or living roofs, are a layer grown on a rooftop. It can help save energy by providing insulation for buildings and removing heat from the air. This insulation can help keep buildings cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter, reducing the need for heating and air conditioning. The temperature in green roofs can be 1-4.5° Celsius lower than those of conventional roofs and also reduce city temperatures.
The amount of energy savings that can be achieved with a green roof depends on several factors, including the climate, the type of vegetation used, and the design and construction of the roof. In general, green roofs can provide energy savings of up to 25% for heating and cooling.
However, in some cases, the savings can be even higher. It’s important to consult with a professional when designing and installing a green roof to ensure that it effectively provides energy savings.
Does green energy help reduce carbon emissions?
Buying green energy can help support the development of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, which can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and associated carbon emissions.
By purchasing green energy, you can help drive demand for renewable energy and support the transition to a more sustainable energy system. This, in turn, can help reduce the overall environmental impact of our energy consumption. In addition, many green energy sources, such as wind and solar power, are becoming increasingly competitive with traditional fossil fuel-based sources of energy, so buying green energy can also be a cost-effective option in some cases.

Dr. Erik Wallin
Chief Ecosystem Officer, and founder of ProptechOS and RealEstateCore is recognized as a leader in Building Operating Systems (BOS) and making the buildings of the world smarter. He holds an MSc and a Ph.D. in Media and Computer Science from KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
Read his full bio and information here.